The oil pump in your vehicle is a crucial component that circulates lubricating oil throughout the engine. People ask: What are the symptoms of engine oil pump failure? You need to understand that when an oil pump starts to fail, the effects on your engine can be disastrous. Being able to identify symptoms that indicate oil pump problems can help you diagnose issues early and avoid extensive engine damage. This guide covers the signs of a failing oil pump and steps to restore proper lubrication when wear or leaks arise.
Understanding Oil Pump Operation
Before diving into oil pump failure symptoms, let’s review what the oil pump does when working normally:
- Draws oil from the crankcase sump up to the filter.
- Generates flow and pressure to circulate oil through galleys to bearings.
- Regulates oil pressure based on engine speed and demand.
- Provides continuous lubrication during engine operation.
When these vital jobs aren’t performed adequately, such as from pump wear or leakage, critical engine parts won’t receive sufficient lubricating oil. This lack of oil circulation and pressure quickly causes system breakdown.
What Are The Symptoms Of Engine Oil Pump Failure?
Watch for these common symptoms, which show that your oil pump may be having problems:
1. Low Oil Pressure Gauge Readings
The most direct symptom of oil pump issues is low readings on your oil pressure gauge, usually at idle. The minimum pressure should be 5–10 psi when warmed up. Consistently lower readings indicate the pump’s flow is weakening.
2. Oil Pressure Warning Light Illuminated
If your vehicle lacks an actual pressure gauge, the oil pressure warning light coming on when warmed up signals dangerously low levels from pump wear or failure.
3. Engine-Making Knocking or Ticking Sounds
With inadequate oil reaching the valvetrain, camshaft, and bearings, abnormal metallic tapping or knocking noises start resonating from the engine. This indicates components lacking oil film protection.
4. Rough Idle and Acceleration
As bearings and journals dry out internally, loss of oil pressure will make engine operation less smooth. Idle may become choppy or unreliable.
5. Higher Engine Operating Temperature
The circulation of oil also cools internal parts. Reduced flow causes the engine to run hotter as components lose their cooling effect.
6. Check Engine Light Illumination

The computer may detect issues like higher temperatures or combustion changes and trigger the check engine light due to low oil circulation.
7. Metal Debris in Oil Filter and Pan
Once engine parts run dry internally for any period, accelerated wear occurs, putting detectable metallic flakes into the oil pan.
Any of these symptoms indicate dropping oil pressure and volume, requiring prompt diagnosis of the oil pump. Address this promptly to avoid the next level of failure symptoms.
Symptoms of Complete Oil Pump Breakdown

If an oil pump problem is left uncorrected long enough, eventually the pump will fail completely. Symptoms of full failure include:
- Sudden engine shutdown: Without oil pressure, extreme friction will abruptly seize pistons and bearings.
- Failure to restart: After shutdown, a damaged engine will not restart without sufficient lubrication.
- Loud metallic banging or scraping inside the engine: moving parts contacting without oil clearance make harsh mechanical noises before seizures.
- Excess smoke from exhaust or leaks: friction rapidly overheats seals and gaskets, causing external leaks and blue smoke.
Once these signs of full pump failure appear, extensive internal engine damage has likely already occurred. Immediate action is needed to determine repairs.
What Causes Oil Pump Problems?
Now that you can recognize oil pump issues, understanding what causes pump problems helps narrow down root causes.
1. Pump Wear and Mileage
Like all mechanical parts, oil pumps wear internally over time and miles. An eventual loss of pressure indicates a replacement is needed. High-mileage pumps over 100k miles often begin to slip.
2. Poor Oil and Sludge
Thick, sludgy oil and varnish deposits gum up pump mechanisms and restrict flow. Lack of routine oil changes accelerates this.
3. Oil Pump Leaks
External leaks around the pump housing seals and gaskets send oil straight back to the pan rather than through the engine. Watch for oil around the pump and near the front of the engine block.
4. Blocked Pickup Tube
The pump’s pickup tube pulls oil from the pan. A clogged tube screen blocks flow into the pump. Low oil levels can expose the tube.
5. Loose Pump Bolts
If the pump housing is not securely fastened to the block, clearances open up, and the pump loses the pressure needed to properly circulate oil.
6. Broken Pressure Relief Valve
This valve regulates pump pressure. If stuck open due to contamination or spring failure, oil bleeds off without reaching critical components.
Identifying which of these root problems is the culprit is the key to restoring normal lubrication.
Testing Oil Pressure to Diagnose Issues
Suspecting you have an oil pump problem based on symptoms is one thing. But confirming low pressure requires testing before proceeding with repairs. Here are two methods professional technicians use to check real-time oil pressure:
1. Install Temporary Oil Pressure Gauge
A mechanic can remove the oil sender and install a temporary mechanical oil pressure gauge in its place. This gives an accurate PSI reading across the engine RPM range to quantify if pressure is abnormal.
2. Use Diagnostic Oil Pressure Tester
These tools adapt to the oil sender location to electronically simulate engine operating conditions. Minimum pressures can be verified without even running the engine.
These tests conclusively prove if the oil pump is failing to generate standard pressure. Techs rely on them to justify oil pump repairs or replacements. Don’t skip this objective testing.
Restoring Proper Lubrication with Oil Pump Repair
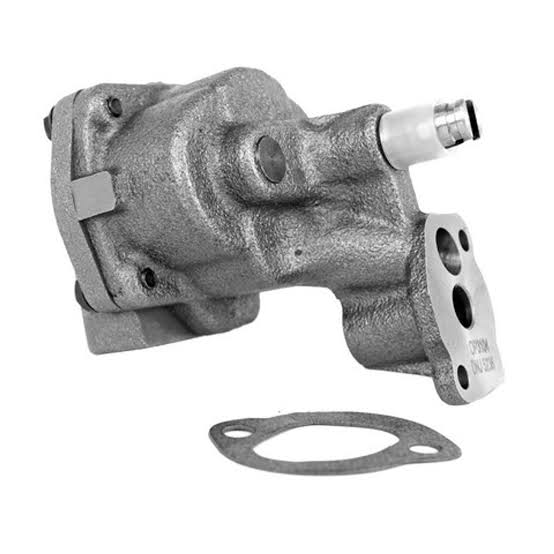

Once low oil pressure is confirmed through testing, solutions depend on the specifics of what’s causing the pump to fail.
- Worn pump: Pump replacement is required. For high-mileage engines, a high-volume pump upgrades protection.
- Sludge contamination: flush the crankcase and clean the pickup tube to restore flow.
- Pump leaks – Replace gaskets and seals or replace entire pump.
- Blocked pickup: remove pickup and flush or reinstall. May need higher oil pan to fully submerge tube.
- Loose bolts: ensure the pump housing is secured to standard torque specs. May need to reseal or replace the pump.
- Stuck pressure relief valve – Requires replacement of oil pressure relief valve.
Proper diagnosis, pressure testing, and addressing the specific fault is crucial. With low mileage, pump repairs may be feasible. But replacement is usually required to completely restore lubrication security on higher-mile engines.
Preventive Maintenance to Maximize Oil Pump Life

While oil pumps eventually need replacement in all vehicles, you can optimize pump lifespan and performance through diligent maintenance.
- Regular oil change, use quality oil to avoid sludge.
- Replace clogged pickup screens. Clean pickup tube bore.
- Use engine oil flush treatment to clean internal deposits.
- Inspect pump leaks early and reseal or replace them as needed.
- Consider a high-volume oil pump if the engine has traveled over 100k miles.
- Verify pump fasteners stay tightened.
- Check operation of oil pressure relief valve.
With proactive care, your stock oil pump should stay trouble-free for over 100,000 miles. But at the first sign of problems, act promptly to avoid significant engine damage from a lack of oil. Pay attention, test pressure, and restore lubrication security.
Wrapping Up
Ignoring early signs of weak oil pump performance risks catastrophic engine damage from oil starvation. Learn the warning symptoms, like low gauge readings and knocking noises. Diagnose the root cause professionally and resolve any leaks, sludge, or worn parts promptly. With vigilant oil system maintenance and inspection, your oil pump will continue supplying vital lubrication throughout your engine’s long service life. Don’t take for granted this critical component that keeps your motor running smoothly.

